Solana基础 - 使用 Solana web3 js 和 Anchor 读取账户数据
本教程详细介绍了如何通过Solana的web3 Javascript客户端直接读取账户数据,并展示了如何在Web应用的前端实现这一功能。教程中首先使用Rust代码初始化并写入数据,然后通过TypeScript读取和反序列化数据,并进一步演示了如何读取由其他Anchor程序创建的账户数据。
本教程展示了如何直接从 Solana web3 Javascript 客户端读取账户数据,以便 web 应用能够在前端读取它。
在上一个教程中,我们使用 solana account <account address> 来读取我们写入的数据,但如果我们正在网站上构建一个 dApp,这种方法是行不通的。
相反,我们必须计算存储账户的地址,读取数据,并从 Solana web3 客户端反序列化数据。
想象一下,如果在 Ethereum 中我们希望避免使用公共变量或视图函数,但仍然想在前端显示它们的值。要在不公开它们或添加视图函数的情况下查看存储变量中的值,我们将使用 getStorageAt(contract_address, slot) API。在 Solana 中,我们将做类似的事情,不过我们只需传入程序的地址,并派生出其存储账户的地址。
以下是上一个教程中的 Rust 代码。它初始化 MyStorage 并使用 set 函数写入 x。在本教程中我们不修改它:
use anchor_lang::prelude::*;
use std::mem::size_of;
declare_id!("GLKUcCtHx6nkuDLTz5TNFrR4tt4wDNuk24Aid2GrDLC6");
#[program]
pub mod basic_storage {
use super::*;
pub fn initialize(ctx: Context<Initialize>) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
pub fn set(ctx: Context<Set>, new_x: u64) -> Result<()> {
ctx.accounts.my_storage.x = new_x;
Ok(())
}
}
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct Set<'info> {
#[account(mut, seeds = [], bump)]
pub my_storage: Account<'info, MyStorage>,
}
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct Initialize<'info> {
#[account(init,
payer = signer,
space=size_of::<MyStorage>() + 8,
seeds = [],
bump)]
pub my_storage: Account<'info, MyStorage>,
#[account(mut)]
pub signer: Signer<'info>,
pub system_program: Program<'info, System>,
}
#[account]
pub struct MyStorage {
x: u64,
}以下是 Typescript 单元测试,它:
- 初始化账户
- 将
170写入存储 - 使用
fetch函数读取值:
import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { BasicStorage } from "../target/types/basic_storage";
describe("basic_storage", () => {
anchor.setProvider(anchor.AnchorProvider.env());
const program = anchor.workspace.BasicStorage as Program;
it("已初始化!", async () => {
const seeds = []
const [myStorage, _bump] = anchor.web3.PublicKey.findProgramAddressSync(seeds, program.programId);
console.log("存储账户地址是", myStorage.toBase58());
await program.methods.initialize().accounts({myStorage: myStorage}).rpc();
await program.methods.set(new anchor.BN(170)).accounts({myStorage: myStorage}).rpc();
// ***********************************
// *** 新代码以读取结构 ***
// ***********************************
let myStorageStruct = await program.account.myStorage.fetch(myStorage);
console.log("x 的值是:", myStorageStruct.x.toString());
});
});
在 Anchor 中查看账户可以使用:
let myStorageStruct = await program.account.myStorage.fetch(myStorage);
console.log("x 的值是:", myStorageStruct.x.toString());
Anchor 会自动计算 `MyStorage` 账户的地址,读取它并将其格式化为 Typescript 对象。
要理解 Anchor 如何神奇地将 Rust 结构转换为 Typescript 结构,我们来看看 `target/idl/basic_storage.json` 中的 IDL。在 JSON 的底部,我们可以看到程序正在创建的结构定义:
"accounts": [
{
"name": "MyStorage",
"type": {
"kind": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"name": "x",
"type": "u64"
}
]
}}
],
**此方法仅适用于你的程序或客户端初始化或创建的账户,并且具有 IDL,不适用于任意账户。**
也就是说,如果你选择 Solana 上的一个随机账户并使用上述代码,反序列化几乎肯定会失败。稍后在本文中,我们将以一种更“原始”的方式读取该账户。
`fetch` 函数并不是魔法。那么,我们如何对于一个我们没有创建的账户进行操作呢?
## 从 Anchor Solana 程序创建的账户中提取数据
如果我们知道另一个用 Anchor 创建的程序的 IDL,我们可以方便地读取其账户数据。
让我们在另一个终端中 `anchor init` 另一个程序,然后让它初始化一个账户,并将该结构中的单个布尔变量设置为 `true`。我们将这个其他账户称为 `other_program`,将存放布尔变量的结构称为 `TrueOrFalse`:
use anchor_lang::prelude::*;
use std::mem::size_of;
declare_id!("4z4dduMSFKFJDnUAKaHnbhHySK8x1PwgArUBXzksjwa8");
[program]
pub mod other_program {
use super::*;
pub fn initialize(ctx: Context<Initialize>) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
pub fn setbool(ctx: Context<SetFlag>, flag: bool) -> Result<()> {
ctx.accounts.true_or_false.flag = flag;
Ok(())
}}
[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct Initialize<'info> {
#[account(mut)]
signer: Signer<'info>,
system_program: Program<'info, System>,
#[account(init, payer = signer, space = size_of::<TrueOrFalse>() + 8, seeds=[], bump)]
true_or_false: Account<'info, TrueOrFalse>,}
[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct SetFlag<'info> {
#[account(mut)]
true_or_false: Account<'info, TrueOrFalse>, }
[account]
pub struct TrueOrFalse {
flag: bool,}
**Typescript 代码:**
import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { OtherProgram } from "../target/types/other_program";
describe("other_program", () => {
anchor.setProvider(anchor.AnchorProvider.env());
const program = anchor.workspace.OtherProgram as Program
it("已初始化!", async () => {
const seeds = []
const [TrueOrFalse, _bump] = anchor.web3.PublicKey.findProgramAddressSync(seeds, program.programId);
console.log("地址: ", program.programId.toBase58());
await program.methods.initialize().accounts({trueOrFalse: TrueOrFalse}).rpc();
await program.methods.setbool(true).accounts({trueOrFalse: TrueOrFalse}).rpc();});
});
在另一个终端中运行 against 的本地区块验证器的测试。注意打印出来的 `programId`。我们需要它来派生 `other_program` 账户的地址。
### 读取程序
在另一个终端中,`anchor init` 另一个程序。我们将其称为 `read`。我们将仅使用 Typescript 代码来读取 `other_program` 的 `TrueOrFalse` 结构,不使用 Rust。这模拟了从另一个程序的存储账户中读取数据。
我们的目录布局如下:
parent_dir/
∟ other_program/
∟ read/
以下代码将从 `other_program` 中读取 `TrueOrFalse` 结构。确保:
- `otherProgramAddress` 与上述打印的地址匹配
- 确保你从正确的文件位置读取 `other_program.json` IDL
- 确保以 `--skip-local-validator` 运行测试,以确保此代码读取其他程序创建的账户
import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
describe("read", () => {
anchor.setProvider(anchor.AnchorProvider.env());
it("读取其他账户", async () => {
// 其他程序的 programId - 确保地址正确
const otherProgramAddress = "4z4dduMSFKFJDnUAKaHnbhHySK8x1PwgArUBXzksjwa8";
const otherProgramId = new anchor.web3.PublicKey(otherProgramAddress);
// 加载其他程序的 idl - 确保路径正确
const otherIdl = JSON.parse(
require("fs").readFileSync("../other_program/target/idl/other_program.json", "utf8")
);
const otherProgram = new anchor.Program(otherIdl, otherProgramId);
const seeds = []
const [trueOrFalseAcc, _bump] =
anchor.web3.PublicKey.findProgramAddressSync(seeds, otherProgramId);
let otherStorageStruct = await otherProgram.account.trueOrFalse.fetch(trueOrFalseAcc);
console.log("flag 的值是:", otherStorageStruct.flag.toString());});
});
预期输出如下: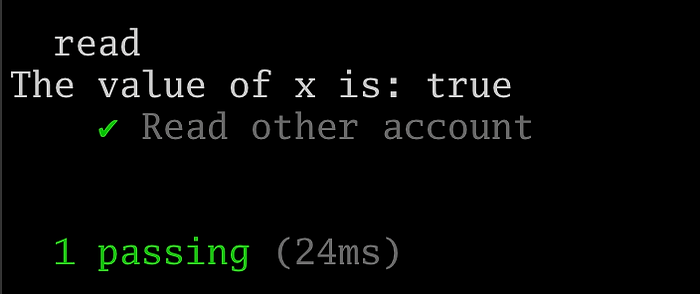
同样,**这仅在其他 Solana 程序是用 Anchor 构建的情况下有效。这是依赖于 Anchor 如何序列化结构。**
## 提取任意账户的数据
在接下来的部分中,我们展示如何在没有 Anchor 魔法的情况下读取数据。
不幸的是,Solana 的 Typescript 客户端文档非常有限,该库已经多次更新,以至于使相关主题的教程过时。
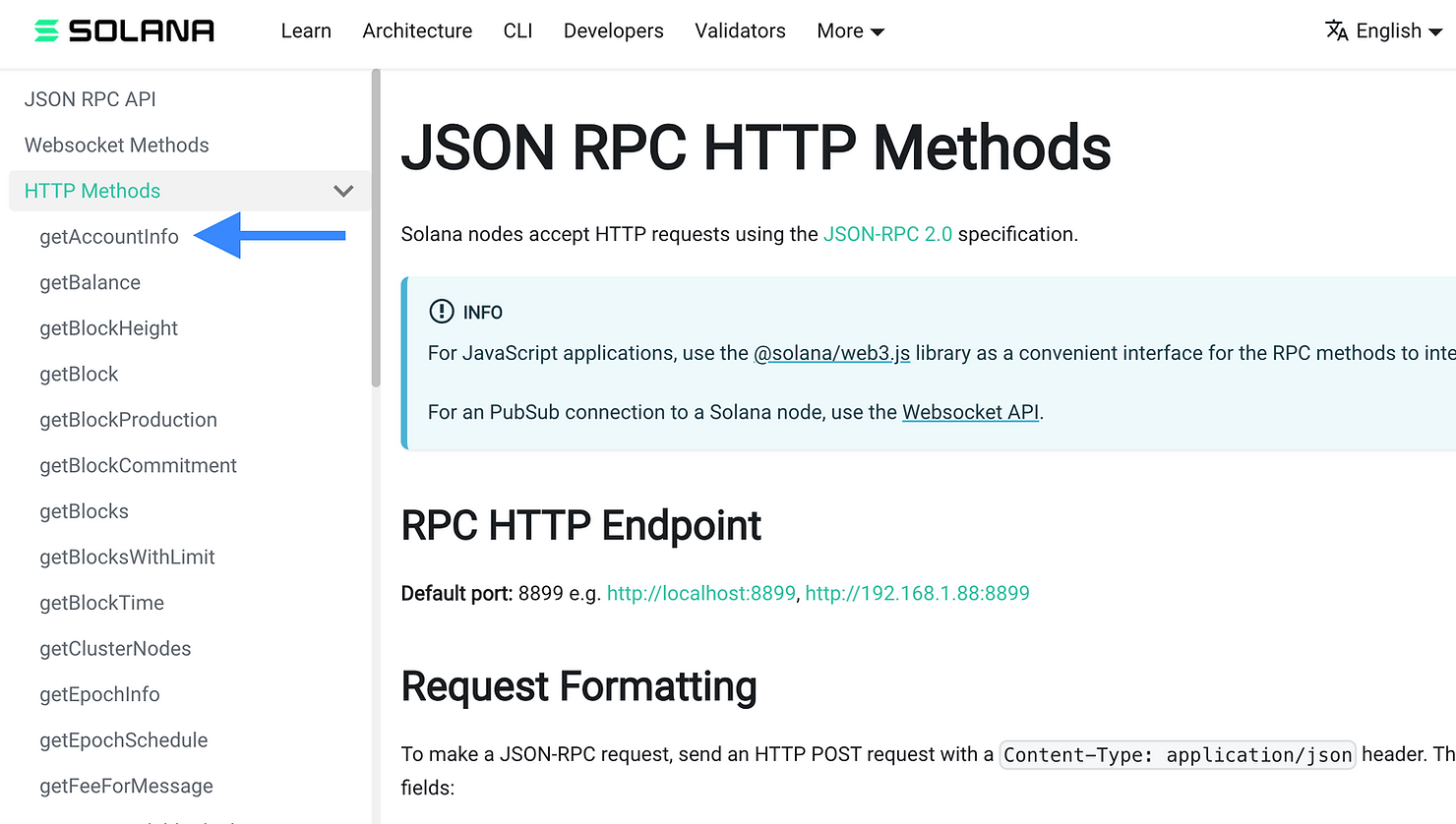
你最好的办法是尝试查找你需要的 Solana web3 Typescript 函数是查阅 [HTTP JSON RPC 方法](https://docs.solana.com/api/http),并寻找一个看起来有希望的方法。在我们看来,`getAccountInfo` 看起来是个不错的选择(蓝色箭头)。
接下来,我们想在 Solana web3 js 中找到该方法。最好使用支持自动补全的 IDE,以便进行尝试直到找到该函数,正如下方视频所示:
<video controls="" style="box-sizing: border-box; display: block; vertical-align: baseline; color: rgb(51, 51, 51); font-family: "PingFang SC", -apple-system, "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, "Hiragino Sans GB", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Microsoft Yahei", sans-serif; font-size: 16px; font-style: normal; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; font-weight: 400; letter-spacing: normal; orphans: 2; text-align: start; text-indent: 0px; text-transform: none; widows: 2; word-spacing: 0px; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px; white-space: normal; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255); text-decoration-thickness: initial; text-decoration-style: initial; text-decoration-color: initial; margin: auto; width: 756px; aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;"></video>
https://img.learnblockchain.cn/2025/02/28/file.mp4
接下来我们展示再次运行测试的预期输出: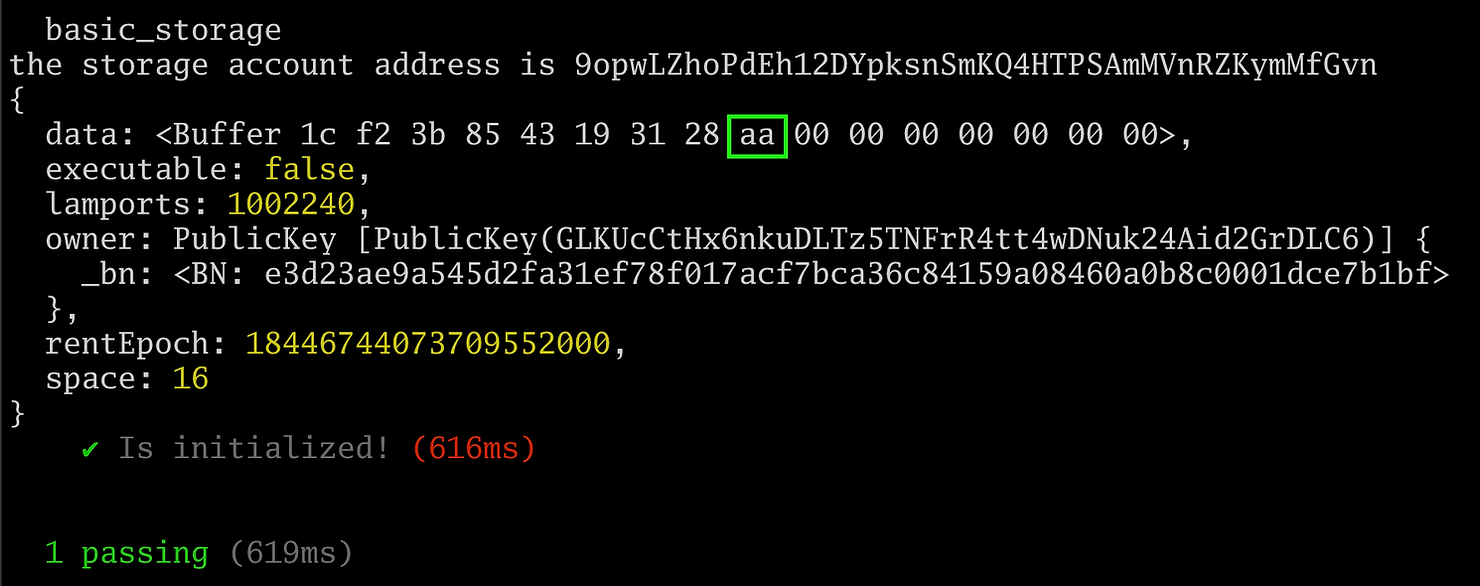
绿色框中的十六进制 `aa` 字节显示我们已成功检索存储在 `set()` 函数中的十进制 `170` 值。
下一步是解析数据缓冲区,这不是我们在这里要涵盖的内容。
**没有强制性的方法来序列化 Solana 账户中的数据**。Anchor 以其自身的方式序列化结构,但如果有人用原生 Rust(没有 Anchor)编写 Solana 程序或使用了自己的序列化算法,那么你就必须根据他们序列化数据的方式自定义反序列化算法。