BOS节点部署,版本升级与测试
昨晚BOSCore已经完成了3秒LIB测试网启动,测试结果是1-3秒内达到不可逆,今天要再进行下中国社区部分的测试。
社区通知消息原文如下
国内社区 3s LIB版本升级演练
BOS 3s LIB测试网已经启动,为了让更多社区成员了解升级流程和特性,中国社区定于北京时间5月15日16:00开始演练,请大家提前做好准备。
此次版本升级的流程:
1.首先启动链时用boscore/bos:v2.0.3版本启动,各位注册bp,出块,模拟现在BOS的网络环境。
2.升级
1)各个bp升级自己的节点版本至新版本,大多数bp升级好后进行下一步
2)bp多签升级系统合约
3)bp多签设置网络升级的块高度:target_number
当lib到达设置的块高度时,共识变为pbft共识,3s可进lib,网络完成升级。
此外,邀请社区开发者对昨晚的lib-testnet做公开测试,发现问题者可以在github上提出issue,最终会根据大家提出的issue奖励BOS,最高奖励 1000 BOS 欢迎大家踊跃参与进来!!!可以加入:https://t.me/BOSTestnet
会议链接:
主题:BOS中国社区3s LIB版本升级演练
时间:五月 15, 2019 4:00 下午 北京,上海
加入 Zoom 会议
https://zoom.us/j/353729204
大家可以提前将自己的bp名字和公钥发给我,网络启动时帮大家创建好。前段时间一直在忙,没有参与,只是默默围观,今天单独抽出时间参与下。
从技术方面来说,如果此方案稳定可行的话,对当前公司项目用户体验,可以有极大的提升。
环境准备
节点搭建对比EOS的来说,基本没差别,我们简单的记录下
准备个简单配置的测试机器
- CPU: 4核
- RAM: 8G
- 地点: 香港阿里云
下载和编译代码
下载代码
git clone https://github.com/boscore/bos.git
git checkout -b v2.0.3编译
cd bos/
git submodule update --init --recursive
./eosio_build.sh -s BOS安装
sudo ./eosio_install.sh配置节点
先运行下nodeos 初始化创建config.ini
配置config.ini
增加 p2p-peer-address
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.48.230:5016 #abp
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.107.217:2022
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.48.230:2018 #abp
p2p-peer-address = 3.1.39.190:10772 #blockedencom
p2p-peer-address = 47.52.101.176:9476 #itokenpocket
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.48.230:2018 #abp
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.48.230:5016 #abp
p2p-peer-address = 47.75.107.217:2022 # saylovetomom
p2p-peer-address = 15.164.99.58:9876 #starteosiobp其余配置参考《从零开始,纯净机器上部署EOS测试网 (版本v1.4.1)》
创建genesis.json
{
"initial_timestamp": "2019-05-15T00:30:00.000",
"initial_key": "EOS6YFfrYZ3z7bNnzoZF4V2zJStudMJ4NJBBE1JXGzebVzMG9aLc7",
"initial_configuration": {
"max_block_net_usage": 1048576,
"target_block_net_usage_pct": 1000,
"max_transaction_net_usage": 524288,
"base_per_transaction_net_usage": 12,
"net_usage_leeway": 500,
"context_free_discount_net_usage_num": 20,
"context_free_discount_net_usage_den": 100,
"max_block_cpu_usage": 200000,
"target_block_cpu_usage_pct": 1000,
"max_transaction_cpu_usage": 150000,
"min_transaction_cpu_usage": 100,
"max_transaction_lifetime": 3600,
"deferred_trx_expiration_window": 600,
"max_transaction_delay": 3888000,
"max_inline_action_size": 4096,
"max_inline_action_depth": 4,
"max_authority_depth": 6
}
}模拟现在BOS的网络环境
此时运行nodeos --genesis-json 加上面genesis.json的路径,启动节点,此时能正常接收其他节点的出块。
注册BP节点,并被投票,成为出块节点
升级节点,更新共识协议
升级节点到最新版本
当前最新版本v3.0.0-rc3
git checkout -b v3.0.0-rc3同上,编译,并安装,重新启动。
升级系统合约
新版本的系统合约:https://github.com/boscore/bos.contracts
cleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 set contract eosio ./eosio.system/ -p eosio -s -j -d > updatasystem.jsoncleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig propose_trx updatesystem bppermission1.json updatesystem.json bosstorebestcleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig approve bosstorebest updatesystem '{"actor":"bosstorebest","permission":"active"}' -p bosstorebestcleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig exec bosstorebest updatesystem -p bosstorebest@activecleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig review bosstorebest updatesystemcleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 get table eosio.msig bosstorebest approvals2设置升级块高度提案
cleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 push action eosio setupgrade '{"up":{"target_block_num":21000}}' -p eosio -s -j -d > setnum.jsoncleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig propose_trx setnum bppermission1.json setnum.json bosstorebestcleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig approve bosstorebest setnum '{"actor":"bosstorebest","permission":"active"}' -p bosstorebestcleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 multisig exec bosstorebest setnum -p bosstorebest@active查询设置的升级块高度
cleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 get table eosio eosio upgrade
{
"rows": [{
"target_block_num": 21000
}
],
"more": false
}
设置块高度时
达到设定的高度时输出以下log
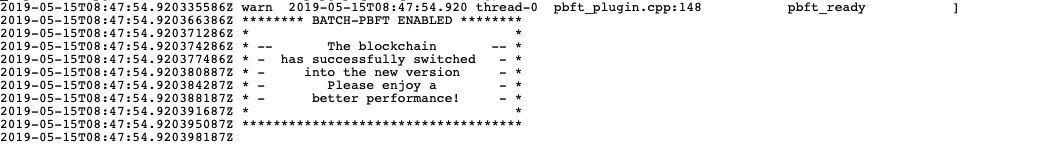
表示升级成功了。
查询区块块信息
surou@DESKTOP-444S803:/mnt/c/Users/Surou$ cleos -u http://47.75.48.230:5015 get info
{
"server_version": "82de16b9",
"chain_id": "5c70c434cfd0ae8a2fde509fd452f8f64236ac120ba81631b239fb4bd1b1e2c3",
"head_block_num": 29732,
"last_irreversible_block_num": 29731,
"last_irreversible_block_id": "000074234261f645187eae528b720577235d5bd306efb6a11906976c725e5583",
"head_block_id": "00007424d2c9aecdf90f1e123c4ffbe4c30e14ce9428cffa18c70bda981de290",
"head_block_time": "2019-05-15T10:02:49.000",
"head_block_producer": "bospacificbp",
"current_view": 0,
"target_view": 1,
"last_stable_checkpoint_block_num": 29701,
"virtual_block_cpu_limit": 200000000,
"virtual_block_net_limit": 1048576000,
"block_cpu_limit": 199900,
"block_net_limit": 1048576,
"server_version_string": "v3.0.0-rc2-21-g82de16b98"
}最新区块与不可逆块数,相差1块,此时不可逆确认时间间隔为0.5s
参考
常见问题
- "RdKafka::rdkafka" but the target was not found
https://www.bcskill.com/index.php/archives/604.html
特别感谢 shiqi@eostore小妹妹补充的信息。
EOS源码分析之八区块及数据结构
eos源码分析之八区块及数据结构
做为EOS系列的最后一篇,把区块及相关的数据结构分析一下。虽然在前面的共识中分析过出块这部分,但对EOS的区块结构及一些细节并没有深入进去。
一、区块
EOS的区块设计不同的版本变化很大,这里以4.0的为模板分析,先看一下它的数据结构:
struct block_header
{
block_timestamp_type timestamp;
account_name producer;//帐户标识符 13字节
uint16_t confirmed = 1;
block_id_type previous;//前一块的HASH
checksum256_type transaction_mroot; /// mroot of cycles_summary
checksum256_type action_mroot; /// mroot of all delivered action receipts
uint32_t schedule_version = 0;
optional<producer_schedule_type> new_producers;//新生产者
extensions_type header_extensions;
digest_type digest()const;//摘要哈希
block_id_type id() const; //自己的哈希
uint32_t block_num() const { return num_from_id(previous) + 1; }
static uint32_t num_from_id(const block_id_type& id);//ID是任意数字,区块号是从零长到现在的排序号 ID=HASH+n
};
struct signed_block_header : public block_header
{
signature_type producer_signature;//生产者签名
};
struct signed_block : public signed_block_header {
using signed_block_header::signed_block_header;
signed_block() = default;
signed_block( const signed_block_header& h ):signed_block_header(h){}
vector<transaction_receipt> transactions; /// new or generated transactions交易记录
extensions_type block_extensions;//扩展区
};
using signed_block_ptr = std::shared_ptr<signed_block>;//重定义一个新的数据类型,方便使用
这里感觉最大的不同是把原来的交易ID直接弄成了交易内容,这样有点简单粗暴的感觉,但是确实是容易理解一些。区块的生产在前面选举后分析过,这里不再赘述,看一下产生区块中对交易的处理。
二、交易和上链
正如所有的区块链一样,交易最终打包入区块,才是真正的区块成功能,也就是说,区块生产出来的目的不是单纯生产块,而要把交易数据打包进去,然后再保存到数据库,最终上链。
1、交易
transaction_trace_ptr push_transaction( const transaction_metadata_ptr& trx,
fc::time_point deadline,
bool implicit,
uint32_t billed_cpu_time_us )
{
FC_ASSERT(deadline != fc::time_point(), "deadline cannot be uninitialized");
transaction_trace_ptr trace;//交易检索
try {
transaction_context trx_context(self, trx->trx, trx->id); //交易管理控制
trx_context.deadline = deadline;
trx_context.billed_cpu_time_us = billed_cpu_time_us;
trace = trx_context.trace;
try {
if( implicit ) {
trx_context.init_for_implicit_trx();
} else {
trx_context.init_for_input_trx( trx->packed_trx.get_unprunable_size(),
trx->packed_trx.get_prunable_size(),
trx->trx.signatures.size() );
}
//检查权限集合
if( !implicit && pending->_block_status == controller::block_status::incomplete ) {
check_actor_list( trx_context.bill_to_accounts ); // Assumes bill_to_accounts is the set of actors authorizing the transaction
}
//延迟状态
trx_context.delay = fc::seconds(trx->trx.delay_sec);
//检查权限,这个前面分析过
if( !self.skip_auth_check() && !implicit ) {
authorization.check_authorization(
trx->trx.actions,
trx->recover_keys( chain_id ),
{},
trx_context.delay,
[](){}
/*std::bind(&transaction_context::add_cpu_usage_and_check_time, &trx_context,
std::placeholders::_1)*/,
false
);
}
//执行上下文,其实就是执行tx中的action
trx_context.exec();
trx_context.finalize(); // Automatically rounds up network and CPU usage in trace and bills payers if successful
//创建恢复点
auto restore = make_block_restore_point();
if (!implicit) {
transaction_receipt::status_enum s = (trx_context.delay == fc::seconds(0))
? transaction_receipt::executed
: transaction_receipt::delayed;
//交易填充
trace->receipt = push_receipt(trx->packed_trx, s, trx_context.billed_cpu_time_us, trace->net_usage);
pending->_pending_block_state->trxs.emplace_back(trx);
} else {
transaction_receipt_header r;
r.status = transaction_receipt::executed;
r.cpu_usage_us = trx_context.billed_cpu_time_us;
r.net_usage_words = trace->net_usage / 8;
trace->receipt = r;
}
//填充ACTION
fc::move_append(pending->_actions, move(trx_context.executed));
// call the accept signal but only once for this transaction
if (!trx->accepted) {
emit( self.accepted_transaction, trx);
trx->accepted = true;
}
emit(self.applied_transaction, trace);// 发送成功打包交易的消息
trx_context.squash();//不敢肯定,是不是清理回退的数据
restore.cancel();//取消恢复
if (!implicit) {
unapplied_transactions.erase( trx->signed_id );
}
return trace;
} catch (const fc::exception& e) {
trace->except = e;
trace->except_ptr = std::current_exception();
}
if (!failure_is_subjective(*trace->except)) {
unapplied_transactions.erase( trx->signed_id );
}
return trace;
} FC_CAPTURE_AND_RETHROW((trace))
}2、上链
在apply_block中:
void commit_block( bool add_to_fork_db ) {
if( add_to_fork_db ) {
pending->_pending_block_state->validated = true;
auto new_bsp = fork_db.add( pending->_pending_block_state );
emit( self.accepted_block_header, pending->_pending_block_state );
head = fork_db.head();
FC_ASSERT( new_bsp == head, "committed block did not become the new head in fork database" );
}
// ilog((fc::json::to_pretty_string(*pending->_pending_block_state->block)));
emit( self.accepted_block, pending->_pending_block_state );
if( !replaying ) {
reversible_blocks.create<reversible_block_object>( [&]( auto& ubo ) {
ubo.blocknum = pending->_pending_block_state->block_num;
ubo.set_block( pending->_pending_block_state->block );
});
}
pending->push();
pending.reset();//恢复状态,可以再次出块
}
通过fork_db的操作把数据库存储起来,然后挂到链上,形成区块链。再广播出去,清除状态,重新准备出块。
三、相关的几个数据结构
有几个数据结构比较重要:multi_index,optional和scoped_exit。
1、访问数据库的multi_index
template<uint64_t TableName, typename T, typename... Indices>
class multi_index
{
private:
static_assert( sizeof...(Indices) <= 16, "multi_index only supports a maximum of 16 secondary indices" );
constexpr static bool validate_table_name( uint64_t n ) {
// Limit table names to 12 characters so that the last character (4 bits) can be used to distinguish between the secondary indices.
return (n & 0x000000000000000FULL) == 0;
}
constexpr static size_t max_stack_buffer_size = 512;
static_assert( validate_table_name(TableName), "multi_index does not support table names with a length greater than 12");
uint64_t _code;
uint64_t _scope;
mutable uint64_t _next_primary_key;
enum next_primary_key_tags : uint64_t {
no_available_primary_key = static_cast<uint64_t>(-2), // Must be the smallest uint64_t value compared to all other tags
unset_next_primary_key = static_cast<uint64_t>(-1)
};
struct item : public T
{
template<typename Constructor>
item( const multi_index* idx, Constructor&& c )
:\__idx(idx){
c(\*this);
}
......
};
struct item_ptr
{
item_ptr(std::unique_ptr<item>&& i, uint64_t pk, int32_t pitr)
: \_item(std::move(i)), \_primary_key(pk), \_primary_itr(pitr) {}
......
};
mutable std::vector<item_ptr> _items_vector;
template<uint64_t IndexName, typename Extractor, uint64_t Number, bool IsConst>
struct index {
public:
typedef Extractor secondary_extractor_type;
typedef typename std::decay<decltype( Extractor()(nullptr) )>::type secondary_key_type;
......
constexpr static uint64_t name() { return index_table_name; }
constexpr static uint64_t number() { return Number; }
struct const_iterator : public std::iterator<std::bidirectional_iterator_tag, const T> {
public:
friend bool operator == ( const const_iterator& a, const const_iterator& b ) {
return a.\_item == b.\_item;
}
friend bool operator != ( const const_iterator& a, const const_iterator& b ) {
return a.\_item != b.\_item;
}
const T& operator*()const { return *static_cast<const T*>(\_item); }
const T* operator->()const { return static_cast<const T*>(\_item); }
......
return *this;
}
const_iterator& operator--() {
using namespace \_multi_index_detail;
......
return \*this;
}
const_iterator():_item(nullptr){}
private:
friend struct index;
const_iterator( const index* idx, const item* i = nullptr )
: _idx(idx), _item(i) {}
const index* _idx;
const item* _item;
}; /// struct multi_index::index::const_iterator
typedef std::reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
const_iterator cbegin()const {
using namespace \_multi_index_detail;
return lower_bound( secondary_key_traits<secondary_key_type>::lowest() );
}
......
const T& get( secondary_key_type&& secondary, const char* error_msg = "unable to find secondary key" )const {
return get( secondary, error_msg );
}
// Gets the object with the smallest primary key in the case where the secondary key is not unique.
const T& get( const secondary_key_type& secondary, const char* error_msg = "unable to find secondary key" )const {
auto result = find( secondary );
eosio_assert( result != cend(), error_msg );
return *result;
}
const_iterator lower_bound( secondary_key_type&& secondary )const {
return lower_bound( secondary );
}
const_iterator lower_bound( const secondary_key_type& secondary )const {
using namespace \_multi_index_detail;
......
return {this, &mi};
}
const_iterator upper_bound( secondary_key_type&& secondary )const {
return upper_bound( secondary );
}
const_iterator upper_bound( const secondary_key_type& secondary )const {
......
return {this, &mi};
}
const_iterator iterator_to( const T& obj ) {
......
return {this, &objitem};
}
......
static auto extract_secondary_key(const T& obj) { return secondary_extractor_type()(obj); }
private:
friend class multi_index;
index( typename std::conditional<IsConst, const multi_index*, multi_index*>::type midx )
:_multidx(midx){}
typename std::conditional<IsConst, const multi_index*, multi_index*>::type _multidx;
}; /// struct multi_index::index
......
const item* ptr = itm.get();
auto pk = itm->primary_key();
auto pitr = itm->__primary_itr;
_items_vector.emplace_back( std::move(itm), pk, pitr );
return *ptr;
} /// load_object_by_primary_iterator
public:
multi_index( uint64_t code, uint64_t scope )
:_code(code),_scope(scope),_next_primary_key(unset_next_primary_key)
{}
......
_item = &_multidx->load_object_by_primary_iterator( prev_itr );
return *this;
}
private:
const_iterator( const multi_index* mi, const item* i = nullptr )
:_multidx(mi),_item(i){}
const multi_index* _multidx;
const item* _item;
friend class multi_index;
}; /// struct multi_index::const_iterator
typedef std::reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
const_iterator cbegin()const {
return lower_bound(std::numeric_limits<uint64_t>::lowest());
}
const_iterator begin()const { return cbegin(); }
.......
void erase( const T& obj ) {
using namespace \_multi_index_detail;
......
hana::for_each( \_indices, [&]( auto& idx ) {
typedef typename decltype(+hana::at_c<0>(idx))::type index_type;
auto i = objitem.__iters[index_type::number()];
if( i < 0 ) {
typename index_type::secondary_key_type secondary;
i = secondary_index_db_functions<typename index_type::secondary_key_type>::db_idx_find_primary( \_code, \_scope, index_type::name(), objitem.primary_key(), secondary );
}
if( i >= 0 )
secondary_index_db_functions<typename index_type::secondary_key_type>::db_idx_remove( i );
});
}
};
multi_index这个数据结构同样是仿照BOOST库中的boost::multi_index;估计EOS的开发人员觉得这个太重,自己搞了一个,当然,顺带实现很多自己独立的需求。需要说明的是WIKI上的说明是比较落后的,而且EOS开发团队也声明了,这个容器对象是不断演进的,所以说现在分析的可能已经是落后的了,但可能他们的大原则不会有剧烈的变动。
EOS为每个账户都预留了数据库空间(大小与代币持有量有关),账户可以建立多个数据表。智能合约无法直接操作存储在见证人硬盘中的数据表,需要使用multi_index作为中间工具(或者叫容器),每个multi_index实例都与一个特定账户的特定数据表进行交互(取决于实例化时的参数)。
这个多索引表有几个特点:类似ORM中的映射表,行为独立的对象,列为属性;有主键和非主键,排序时默认为升序,同样主键只能唯一并为uint64_t类型;支持自定函数做为索引,但返回值受限,即只能为支持的键类型;允许多索引排序,但是二级索引不大于16,前面的代码可以看到,同时不支持二级索引的直接构建;类似双向链表可以双向迭代。
它支持主要以下几种操作:
emplace:添加一个对象(row)到表中,返回一个新创建的主键迭代器。在这个过程中创建新对象,序列化写入表中,更新二级索引,付费。如果出现异常则直接抛出。
erase:这个就简单了,直接擦除。可以用迭代器也可以引用对象来删除。删除后返回之后的迭代器,并更新相关索引及费用。
modify:类似于数据库的UPDATE,这个比较麻烦,需要提供更新对象的迭代器,更新对象的引用,帐户(需要付费的)以及更新目标对象的函数(lambada),无返回值,在操作过程中主要是要对payer的属性进行判断,然后进行费用的计算和相关退费,完成后更新索引。
get:由主键查找对象,返回对象的引用,如果没找到,抛出异常。
find:根据主键查找已存在的对象。它的返回值是一个迭代器。如果没有查到返回一个end迭代器。
迭代器有点类似于STD标准库的迭代器,可以前后遍历,这里不再赘述。
2、类boost::optional的自定义容器
/**
* @brief provides stack-based nullable value similar to boost::optional
*
* Simply including boost::optional adds 35,000 lines to each object file, using
* fc::optional adds less than 400.
*/
template<typename T>
class optional
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef typename std::aligned_storage<sizeof(T), alignof(T)>::type storage_type;
optional():\_valid(false){}
~optional(){ reset(); }
optional( optional& o )
:_valid(false)
{
if( o._valid ) new (ptr()) T( *o );
\_valid = o._valid;
}
......
template<typename U>
optional( const optional<U>& o )
:_valid(false)
{
if( o._valid ) new (ptr()) T( *o );
\_valid = o._valid;
}
template<typename U>
optional( optional<U>& o )
:_valid(false)
{
if( o._valid )
{
new (ptr()) T( *o );
}
\_valid = o._valid;
}
template<typename U>
optional( optional<U>&& o )
:_valid(false)
{
if( o._valid ) new (ptr()) T( fc::move(*o) );
\_valid = o._valid;
o.reset();
}
......
optional& operator=( optional&& o )
{
if (this != &o)
{
if( \_valid && o._valid )
{
ref() = fc::move(*o);
o.reset();
} else if ( !\_valid && o._valid ) {
\*this = fc::move(*o);
} else if (\_valid) {
reset();
}
}
return \*this;
}
friend bool operator < ( const optional a, optional b )
{
if( a.valid() && b.valid() ) return \*a < \*b;
return a.valid() < b.valid();
}
......
void reset()
{
if( \_valid )
{
ref().~T(); // cal destructor
}
\_valid = false;
}
private:
template<typename U> friend class optional;
T& ref() { return \*ptr(); }
const T& ref()const { return *ptr(); }
T* ptr() { return reinterpret_cast<T*>(&\_value); }
const T* ptr()const { return reinterpret_cast<const T\*>(&\_value); }
bool _valid;
storage_type _value;
};
这个其实不能称做一个容器,因为它一般只盛放一个数据结构,它的主要目的标题也很清楚,其实是老大们不愿意使用BOOST的相关代码,太多了,这个才几百行,小巧实用。
这个模板类的主要作用是封装一些数据结构,防止未初始化或者无意义的数据表达不清楚。比如一些返回值是NULL,有EOF,还有一些是string::npos等等,封装起来就是为了起一个标准的作用,其实你看这个类内部,并没有太多的真正意义的自己操作的数据,大多还是原生数据结构的使用。
3、范围控制的scoped_exit
template<typename Callback>
class scoped_exit {
public:
template<typename C>
scoped_exit( C&& c ):callback( std::forward<C>(c) ){}
scoped_exit( scoped_exit&& mv )
:callback( std::move( mv.callback ) ),canceled(mv.canceled)
{
mv.canceled = true;
}
scoped_exit( const scoped_exit& ) = delete;
scoped_exit& operator=( const scoped_exit& ) = delete;
~scoped_exit() {
if (!canceled)
try { callback(); } catch( ... ) {}
}
scoped_exit& operator = ( scoped_exit&& mv ) {
if( this != &mv ) {
~scoped_exit();
callback = std::move(mv.callback);
canceled = mv.canceled;
mv.canceled = true;
}
return \*this;
}
void cancel() { canceled = true; }
private:
Callback callback;
bool canceled = false;
};
template<typename Callback>
scoped_exit<Callback> make_scoped_exit( Callback&& c ) {
return scoped_exit<Callback>( std::forward<Callback>(c) );
}
这个类其实也得很有趣,如果对RAII比较了解的话,这个其实有一点变相的意思,在离开某个范围时,调用这个数据结构的析构函数,然后调用指定的回调函数来处理一些相关的事情,比如清理一些内存等等。
这里的模板构造函数用到了std::forward
其实EOS中的数据结构和编程方式还是有些复杂的,特别是其中一些使用了比较传统的宏模板自动创建的方法(在MFC中常见,但广受诟病),所以一些代码还是比较晦涩的,不建议也这样使用。
EOS源码分析之七钱包和帐户
eos源码分析之七钱包和帐户
一、EOS的钱包帐户
EOS的钱包其实主要就是管理密钥对,因为他不负责产生地址,也就是说,不会像以前的以太坊或者比特币,要通过密钥来产生钱包地址。它主要是提供对帐户的签名管理,也就是前面说的签名需要的密钥进行管理。
EOS使用是非UTXO机制,即帐户机制,这点和以太坊相同,但是他们又有不同之处,EOS为了使用安全方便,引入了权限和角色的功能。通过不同的帐户和私钥进行组合,可以达到创建不同的权限的帐户动作。举一个例子,你可以把你自己的帐户处理动作分配给任意的人,那么那个人就拥有了你的所有的帐户动作,但是它仍然是使用自己的密钥对来对你分配的动作进行签名。
要创建帐户,首先要创建钱包,因为创建帐户需要创建钱包时产生的密钥对。
//创建钱包
string wallet_name = "default";
auto createWallet = wallet->add_subcommand("create", localized("Create a new wallet locally"), false);
createWallet->add_option("-n,--name", wallet_name, localized("The name of the new wallet"), true);
createWallet->set_callback([&wallet_name] {
// wait for keosd to come up
try_port(uint16_t(std::stoi(parse_url(wallet_url).port)), 2000);
const auto& v = call(wallet_url, wallet_create, wallet_name);
std::cout << localized("Creating wallet: ${wallet_name}", ("wallet_name", wallet_name)) << std::endl;
std::cout << localized("Save password to use in the future to unlock this wallet.") << std::endl;
std::cout << localized("Without password imported keys will not be retrievable.") << std::endl;
std::cout << fc::json::to_pretty_string(v) << std::endl;
});
//因为创建帐户需要创建钱包时产生的密钥对
// create key
create->add_subcommand("key", localized("Create a new keypair and print the public and private keys"))->set_callback( [](){
auto pk = private_key_type::generate();
auto privs = string(pk);
auto pubs = string(pk.get_public_key());
std::cout << localized("Private key: ${key}", ("key", privs) ) << std::endl;
std::cout << localized("Public key: ${key}", ("key", pubs ) ) << std::endl;
});
//创建帐户
struct create_account_subcommand {
string creator;
string account_name;
string owner_key_str;
string active_key_str;
string stake_net;
string stake_cpu;
uint32_t buy_ram_bytes_in_kbytes = 0;
string buy_ram_eos;
bool transfer;
bool simple;
create_account_subcommand(CLI::App* actionRoot, bool s) : simple(s) {
auto createAccount = actionRoot->add_subcommand( (simple ? "account" : "newaccount"), localized("Create an account, buy ram, stake for bandwidth for the account"));
createAccount->add_option("creator", creator, localized("The name of the account creating the new account"))->required();
createAccount->add_option("name", account_name, localized("The name of the new account"))->required();
//这里需要两个KEY
createAccount->add_option("OwnerKey", owner_key_str, localized("The owner public key for the new account"))->required();
createAccount->add_option("ActiveKey", active_key_str, localized("The active public key for the new account"));
......
add_standard_transaction_options(createAccount);
createAccount->set_callback([this] {
if( !active_key_str.size() )
active_key_str = owner_key_str;
public_key_type owner_key, active_key;
try {
owner_key = public_key_type(owner_key_str);
} EOS_RETHROW_EXCEPTIONS(public_key_type_exception, "Invalid owner public key: ${public_key}", ("public_key", owner_key_str));
try {
active_key = public_key_type(active_key_str);
} EOS_RETHROW_EXCEPTIONS(public_key_type_exception, "Invalid active public key: ${public_key}", ("public_key", active_key_str));
auto create = create_newaccount(creator, account_name, owner_key, active_key);//创建一个帐户
.......
});
}
};
chain::action create_newaccount(const name& creator, const name& newaccount, public_key_type owner, public_key_type active) {
return action {
tx_permission.empty() ? vector<chain::permission_level>{{creator,config::active_name}} : get_account_permissions(tx_permission),
eosio::chain::newaccount{//调用帐户创建
.creator = creator,
.name = newaccount,
.owner = eosio::chain::authority{1, {{owner, 1}}, {}},
.active = eosio::chain::authority{1, {{active, 1}}, {}}
}
};
}
整体的步骤来说就是创建钱包,创建密钥,导入密钥到钱包,由密钥来创建帐户。看代码中还有一个直接在钱包中创建密钥的命令。
旧的帐户的管理在插件account_history_plugin中。它提供了一个接口插件account_history_api_plugin用来更方便的管理帐户的历史记录。同样,在历史记录的类管理里中,使用了account_history_plugin_impl类来真正提供历史记录的控制。
但是在新的版本中,用history_plugin替代了它,相应的接口也替换成了history_api_plugin.这里面主要涉及到了以下几个类(排除api接口类):history_plugin_impl,这个类是真正的操作数据的类,所有的关于历史记录的动作,最终都要落在这个类中。history_plugin是插件增加的实体类,是调用history_plugin_impl的入口点。read_only类是真正处理数据的类。
这里看一个帐户的交易记录读取:
read_only::get_transaction_result read_only::get_transaction( const read_only::get_transaction_params& p )const {
auto& chain = history->chain_plug->chain();//获得当前指定的Controller
get_transaction_result result;
result.id = p.id;
result.last_irreversible_block = chain.last_irreversible_block_num();
const auto& db = chain.db();//获得当前数据库的句柄
//得到并处理multiindex的结果
const auto& idx = db.get_index<action_history_index, by_trx_id>();
auto itr = idx.lower_bound( boost::make_tuple(p.id) );
if( itr == idx.end() ) {
return result;
}
result.id = itr->trx_id;
result.block_num = itr->block_num;
result.block_time = itr->block_time;
if( fc::variant(result.id).as_string().substr(0,8) != fc::variant(p.id).as_string().substr(0,8) )
return result;
//处理事务action内容
while( itr != idx.end() && itr->trx_id == result.id ) {
fc::datastream<const char*> ds( itr->packed_action_trace.data(), itr->packed_action_trace.size() );
action_trace t;
fc::raw::unpack( ds, t );
result.traces.emplace_back( chain.to_variant_with_abi(t) );
++itr;
}
//处理块
auto blk = chain.fetch_block_by_number( result.block_num );
if( blk == nullptr ) { // still in pending
auto blk_state = chain.pending_block_state();
if( blk_state != nullptr ) {
blk = blk_state->block;
}
}
//得到交易内容
if( blk != nullptr ) {
for (const auto &receipt: blk->transactions) {
if (receipt.trx.contains<packed_transaction>()) {
auto &pt = receipt.trx.get<packed_transaction>();
auto mtrx = transaction_metadata(pt);
if (mtrx.id == result.id) {
fc::mutable_variant_object r("receipt", receipt);
r("trx", chain.to_variant_with_abi(mtrx.trx));
result.trx = move(r);
break;
}
} else {
auto &id = receipt.trx.get<transaction_id_type>();
if (id == result.id) {
fc::mutable_variant_object r("receipt", receipt);
result.trx = move(r);
break;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
//chainbase.hpp
template<typename MultiIndexType>
const generic_index<MultiIndexType>& get_index()const
{
CHAINBASE_REQUIRE_READ_LOCK("get_index", typename MultiIndexType::value_type);
typedef generic_index<MultiIndexType> index_type;
typedef index_type* index_type_ptr;
assert( \_index_map.size() > index_type::value_type::type_id );
assert( \_index_map[index_type::value_type::type_id] );
return *index_type_ptr( \_index_map[index_type::value_type::type_id]->get() );//返回一个multiindex的容器指针
}
这个函数会在history_api_plugin.cpp中由:
void history_api_plugin::plugin_startup() {
ilog( "starting history_api_plugin" );
auto ro_api = app().get_plugin<history_plugin>().get_read_only_api();
//auto rw_api = app().get_plugin<history_plugin>().get_read_write_api();
app().get_plugin<http_plugin>().add_api({
// CHAIN_RO_CALL(get_transaction),
CHAIN_RO_CALL(get_actions),
CHAIN_RO_CALL(get_transaction),
CHAIN_RO_CALL(get_key_accounts),
CHAIN_RO_CALL(get_controlled_accounts)
});
}
提供HTTP的调用,并封装成JSON格式回传给相关调用方。
二、帐户的权限和角色
在前边创建帐户时提到了owner 和 active,它们的权限分别有一个值为1的阈值。owner 和 active 所绑定的 公钥 , 则分别有一个值为1的权重。阈值和权重是什么呢?
阈值是指操作的最小权限,而权重指权限量。简单的说明一下,比如打开保险柜的阈值是3,然后有三个角色权重:1,2,3.则3权重的可以自己直接打开。2和1权重的需要向其它两个角色申请,当权重总和>=3时,才可以打开。
owner是自己的根本权限,可以用来授权给别人的权限。而active是被授予的相关的权限。网上举得例子比较好理解:
owner这个权限比作一扇门,打开这扇门需要一把正确的钥匙。 而 owner 所绑定的那个公钥 对应的那把私钥 就是正确的钥匙。那么二者到底有什么具体的关系和内容呢?
owner:啥都能干,还可以做冷备份。
active:除了不能修改owner之外的所有权限。其它所有的权限都是基于active产生出来的。
帐户的权限在EOS中功能相对来说是比较全的。在EOS中分为单签名帐户和多签名帐户。
1、单签名帐户
因此单签名账户就是权限的阈值和钥匙的权重都为1的一种账户类型。使用某个权限,只需要一把对应的私钥就行了.
struct newaccount {
account_name creator;
account_name name;
authority owner;
authority active;
......
};
单签名其实好理解,其实就是一句话,自己的事情自己干,当然,如果你授权给了别人,别人也可以干,不过不用二者合作,一个即可。
2、多签名帐户
多签名帐户其实就是一个权限绑定了多个帐户或者公钥。要想使用一个权限得需要大于1个以上的签名了。

还是举一个例子,比如有一个权限可以从帐户转走一笔钱,转钱的权限阈值设定为3,有三个角色bob,alice,joe,他们对应的权重为2,2,3.那么joe自己就可以直接操作转钱,而bob,alice由于权重不足,只能二者互相合作或者去向joe申请合作。
它对应到EOS的区块链上,其实就是对帐户的授权,比如某个智能合约需要权限才能操作,那么它会在执行前检查当前帐户的权限,如果不足,则直接退出。否则,完成。
3、密钥的恢复
在EOS中,有一个比较重要的特点就是被盗窃的密钥可以恢复,不会像比特币那样,密钥丢失后所有的一切都永远的消失在区块链中。不过恢复也不是没有条件的:
首先,使用任何30天内的owner权限的密钥和指定的合作伙伴才能恢复。
其次,合作伙伴不参成任何日常交易。合作伙伴其实就是指你的关联帐户。
最后,在恢复的过程中,也可以设置一些类似QQ的恢复机制中的问题机制。
三、签名的验证
既然前面提到了签名需要验证,分析一下验证的过程,从push_transcations中对比一下:
void apply_context::schedule_deferred_transaction( const uint128_t& sender_id, account_name payer, transaction&& trx, bool replace_existing ) {
......
if( !control.skip_auth_check() && !privileged ) { // Do not need to check authorization if replayng irreversible block or if contract is privileged
if( payer != receiver ) {
require_authorization(payer); /// uses payer's storage
}
// if a contract is deferring only actions to itself then there is no need
// to check permissions, it could have done everything anyway.
bool check_auth = false;
for( const auto& act : trx.actions ) {
if( act.account != receiver ) {
check_auth = true;
break;
}
}
if( check_auth ) {
control.get_authorization_manager()
.check_authorization( trx.actions,
{},
{{receiver, config::eosio_code_name}},
delay,
std::bind(&transaction_context::checktime, &this->trx_context),
false
);
}
}
uint32_t trx_size = 0;
auto& d = control.db();
......
trx_context.add_ram_usage( payer, (config::billable_size_v<generated_transaction_object> + trx_size) );
}
void apply_context::require_authorization(const account_name& account,
const permission_name& permission) {
for( uint32_t i=0; i < act.authorization.size(); i++ )
if( act.authorization[i].actor == account ) {
if( act.authorization[i].permission == permission ) {
used_authorizations[i] = true;
return;
}
}
EOS_ASSERT( false, missing_auth_exception, "missing authority of ${account}/${permission}",
("account",account)("permission",permission) );
}
void
authorization_manager::check_authorization( const vector<action>& actions,
const flat_set<public_key_type>& provided_keys,
const flat_set<permission_level>& provided_permissions,
fc::microseconds provided_delay,
const std::function<void()>& \_checktime,
bool allow_unused_keys
)const
{
const auto& checktime = ( static_cast<bool>(\_checktime) ? \_checktime : \_noop_checktime );
auto delay_max_limit = fc::seconds( \_control.get_global_properties().configuration.max_transaction_delay );
auto effective_provided_delay = (provided_delay >= delay_max_limit) ? fc::microseconds::maximum() : provided_delay;
auto checker = make_auth_checker( [&](const permission_level& p){ return get_permission(p).auth; },
\_control.get_global_properties().configuration.max_authority_depth,
provided_keys,
provided_permissions,
effective_provided_delay,
checktime
);
map<permission_level, fc::microseconds> permissions_to_satisfy;
for( const auto& act : actions ) {
bool special_case = false;
fc::microseconds delay = effective_provided_delay;
if( act.account == config::system_account_name ) {
special_case = true;
if( act.name == updateauth::get_name() ) {
check_updateauth_authorization( act.data_as<updateauth>(), act.authorization );
} else if( act.name == deleteauth::get_name() ) {
check_deleteauth_authorization( act.data_as<deleteauth>(), act.authorization );
} else if( act.name == linkauth::get_name() ) {
check_linkauth_authorization( act.data_as<linkauth>(), act.authorization );
} else if( act.name == unlinkauth::get_name() ) {
check_unlinkauth_authorization( act.data_as<unlinkauth>(), act.authorization );
} else if( act.name == canceldelay::get_name() ) {
delay = std::max( delay, check_canceldelay_authorization(act.data_as<canceldelay>(), act.authorization) );
} else {
special_case = false;
}
}
for( const auto& declared_auth : act.authorization ) {
checktime();
if( !special_case ) {
auto min_permission_name = lookup_minimum_permission(declared_auth.actor, act.account, act.name);
if( min_permission_name ) { // since special cases were already handled, it should only be false if the permission is eosio.any
const auto& min_permission = get_permission({declared_auth.actor, \*min_permission_name});
EOS_ASSERT( get_permission(declared_auth).satisfies( min_permission,
\_db.get_index<permission_index>().indices() ),
irrelevant_auth_exception,
"action declares irrelevant authority '${auth}'; minimum authority is ${min}",
("auth", declared_auth)("min", permission_level{min_permission.owner, min_permission.name}) );
}
}
auto res = permissions_to_satisfy.emplace( declared_auth, delay );
if( !res.second && res.first->second > delay) { // if the declared_auth was already in the map and with a higher delay
res.first->second = delay;
}
}
}
// Now verify that all the declared authorizations are satisfied:
// Although this can be made parallel (especially for input transactions) with the optimistic assumption that the
// CPU limit is not reached, because of the CPU limit the protocol must officially specify a sequential algorithm
// for checking the set of declared authorizations.
// The permission_levels are traversed in ascending order, which is:
// ascending order of the actor name with ties broken by ascending order of the permission name.
for( const auto& p : permissions_to_satisfy ) {
checktime(); // TODO: this should eventually move into authority_checker instead
EOS_ASSERT( checker.satisfied( p.first, p.second ), unsatisfied_authorization,
"transaction declares authority '${auth}', "
"but does not have signatures for it under a provided delay of ${provided_delay} ms",
("auth", p.first)("provided_delay", provided_delay.count()/1000)
("delay_max_limit_ms", delay_max_limit.count()/1000)
);
}
if( !allow_unused_keys ) {
EOS_ASSERT( checker.all_keys_used(), tx_irrelevant_sig,
"transaction bears irrelevant signatures from these keys: ${keys}",
("keys", checker.unused_keys()) );
}
}
不过上面的英文注释很搞笑,说其实不必检查,这也是有谁没谁的了。在controller.cpp中push_transcation中也有类似的调用,可以对比分析。这样的情况下基本上帐户和钱包也就分析的差不多了。
EOS源码分析之六共识
eos源码分析之六共识
一、EOS使用的共识
EOS使用的是与传统的共识方法不同的DPOS共识机制,而且在最新的版本中已经更改为了BFT-DPOS机制,在网上看到BM说他又找到了一种更新的共识机制,可以解决被超级节点控制的问题,不知道最终会是什么样子,在比特币和以太坊都使用POW的共识的前提下,EOS使用DPOS机制,可以说是解决高并发的一个比较好的方法。但是,DPOS机制很容易由于节点太少被攻击,事实上也是如此。那么什么是DPOS呢?EOS是怎么使用其进行块之间的共识的呢?
提到dpos,就不得不提到pos,PoS全称Proof of Stake,意为权益证明。说得直白一些就是谁存款多,存款时间长,谁就有权出块(记帐)。这个解决了POW一个痛点,即它不用挖矿,所以也不用耗费老多的电能。但是这这个算法有个致命问题,资本决定了一切,所以很容易被有钱人垄断。
DPOS比POS多了一个D,它的意义是授权,委托。二者的区别是,DPOS需要POS的持有者来通过选举代表,由代表实现出块。而在EOS中则有21个出块者(BP,BlcokProducer),或者叫超级节点。还有101个备份节点。当21个BP的15个确认交易后,交易即不可逆转。
二、共识的过程
1、初始化的共识
EOS初始启动是外在选举的21个超级节点,所以不涉及代码部分。但是一旦启动后会开始新的节点选举,选举成功后,将进行BFT-DPOS共识。
2、选举
主要的代码在contracts/social和eosio.system/voting.cpp中。在cleos的main.cpp中会发现几个数据结构体和相关的应用:
auto registerProducer = register_producer_subcommand(system);
auto unregisterProducer = unregister_producer_subcommand(system);
auto voteProducer = system->add_subcommand("voteproducer", localized("Vote for a producer"));
voteProducer->require_subcommand();
auto voteProxy = vote_producer_proxy_subcommand(voteProducer);
auto voteProducers = vote_producers_subcommand(voteProducer);
auto approveProducer = approve_producer_subcommand(voteProducer);
auto unapproveProducer = unapprove_producer_subcommand(voteProducer);
auto listProducers = list_producers_subcommand(system);
auto delegateBandWidth = delegate_bandwidth_subcommand(system);
auto undelegateBandWidth = undelegate_bandwidth_subcommand(system);
auto listBandWidth = list_bw_subcommand(system);
这些代码会驱动程序在启动后进行相应的动作。选举在EOS中其实也分成两类,即每人独自发起选举,也可以通过代理人代替自己选举,但结果就是本人就无法再投票了。相应的代码如下:
/**
* @pre producers must be sorted from lowest to highest and must be registered and active
* @pre if proxy is set then no producers can be voted for
* @pre if proxy is set then proxy account must exist and be registered as a proxy
* @pre every listed producer or proxy must have been previously registered
* @pre voter must authorize this action
* @pre voter must have previously staked some EOS for voting
* @pre voter->staked must be up to date
*
* @post every producer previously voted for will have vote reduced by previous vote weight
* @post every producer newly voted for will have vote increased by new vote amount
* @post prior proxy will proxied_vote_weight decremented by previous vote weight
* @post new proxy will proxied_vote_weight incremented by new vote weight
*
* If voting for a proxy, the producer votes will not change until the proxy updates their own vote.
*/
//上面的介绍过程挺详细
void system_contract::voteproducer( const account_name voter_name, const account_name proxy, const std::vector<account_name>& producers ) {
require_auth( voter_name );//验证资格
update_votes( voter_name, proxy, producers, true );
}
void system_contract::update_votes( const account_name voter_name, const account_name proxy, const std::vector<account_name>& producers, bool voting ) {
//validate input
if ( proxy ) {//判断是否为代理
eosio_assert( producers.size() == 0, "cannot vote for producers and proxy at same time" );
eosio_assert( voter_name != proxy, "cannot proxy to self" );
require_recipient( proxy );//添加代理帐户
} else {
eosio_assert( producers.size() <= 30, "attempt to vote for too many producers" );
for( size_t i = 1; i < producers.size(); ++i ) { //验证英文注释中的排序
eosio_assert( producers[i-1] < producers[i], "producer votes must be unique and sorted" );
}
}
//验证资格
auto voter = \_voters.find(voter_name);
eosio_assert( voter \!= \_voters.end(), "user must stake before they can vote" ); /// staking creates voter object
eosio_assert( !proxy || !voter->is_proxy, "account registered as a proxy is not allowed to use a proxy" );
/*
* The first time someone votes we calculate and set last_vote_weight, since they cannot unstake until
* after total_activated_stake hits threshold, we can use last_vote_weight to determine that this is
* their first vote and should consider their stake activated.
\*/
//计算权重,用来控制其抵押股权状态,并确定其是否为第一次投票
if( voter->last_vote_weight <= 0.0 ) {
\_gstate.total_activated_stake += voter->staked;
if( \_gstate.total_activated_stake >= min_activated_stake ) {
\_gstate.thresh_activated_stake_time = current_time();
}
}
//计算权重
auto new_vote_weight = stake2vote( voter->staked );
if( voter->is_proxy ) {//是否代理
new_vote_weight += voter->proxied_vote_weight;
}
//处理投票
boost::container::flat_map<account_name, pair<double, bool /*new*/> > producer_deltas;
if ( voter->last_vote_weight > 0 ) {
if( voter->proxy ) {
auto old_proxy = \_voters.find( voter->proxy );
eosio_assert( old_proxy != \_voters.end(), "old proxy not found" ); //data corruption
\_voters.modify( old_proxy, 0, [&]( auto& vp ) {//投票后减去相应权重,对应英文注释
vp.proxied_vote_weight -= voter->last_vote_weight;
});
propagate_weight_change( *old_proxy ); //继续更新相关权重
} else {
//非代理直接操作,一票三十投
for( const auto& p : voter->producers ) {
auto& d = producer_deltas[p];
d.first -= voter->last_vote_weight;
d.second = false;
}
}
}
//处理得票
if( proxy ) {//处理代理
auto new_proxy = \_voters.find( proxy );
eosio_assert( new_proxy != \_voters.end(), "invalid proxy specified" ); //if ( !voting ) { data corruption } else { wrong vote }
eosio_assert( !voting || new_proxy->is_proxy, "proxy not found" );
if ( new_vote_weight >= 0 ) {
\_voters.modify( new_proxy, 0, [&]( auto& vp ) {
vp.proxied_vote_weight += new_vote_weight;
});
propagate_weight_change( *new_proxy );
}
} else {
if( new_vote_weight >= 0 ) {
for( const auto& p : producers ) {
auto& d = producer_deltas[p];
d.first += new_vote_weight;
d.second = true;
}
}
}
// 投票资格验证
for( const auto& pd : producer_deltas ) {
auto pitr = \_producers.find( pd.first );
if( pitr != \_producers.end() ) {
eosio_assert( !voting || pitr->active() || !pd.second.second /* not from new set */, "producer is not currently registered" );
\_producers.modify( pitr, 0, [&]( auto& p ) {
p.total_votes += pd.second.first;
if ( p.total_votes < 0 ) { // floating point arithmetics can give small negative numbers
p.total_votes = 0;
}
\_gstate.total_producer_vote_weight += pd.second.first;
//eosio_assert( p.total_votes >= 0, "something bad happened" );
});
} else {
eosio_assert( !pd.second.second /* not from new set */, "producer is not registered" ); //data corruption
}
}
//更新选举状态
\_voters.modify( voter, 0, [&]( auto& av ) {
av.last_vote_weight = new_vote_weight;
av.producers = producers;
av.proxy = proxy;
});
}
在前面的投票过程中发现,其实要想选举和成为出块者,都需要先行去注册,在最初的Main函数里也提到相应的子命令,那么看一下对应的代码:
/**
* This method will create a producer_config and producer_info object for 'producer'
*
* @pre producer is not already registered
* @pre producer to register is an account
* @pre authority of producer to register
*
*/
void system_contract::regproducer( const account_name producer, const eosio::public_key& producer_key, const std::string& url, uint16_t location ) {
eosio_assert( url.size() < 512, "url too long" );
eosio_assert( producer_key != eosio::public_key(), "public key should not be the default value" );
require_auth( producer );
//查找是否已注册
auto prod = \_producers.find( producer );
if ( prod != \_producers.end() ) { //已注册
if( producer_key != prod->producer_key ) {//已注册,但KEY不同,即同名不同人,修改相关设置
\_producers.modify( prod, producer, [&]( producer_info& info ){
info.producer_key = producer_key;
info.is_active = true;
info.url = url;
info.location = location;
});
}
} else {//全新加入
\_producers.emplace( producer, [&]( producer_info& info ){
info.owner = producer;
info.total_votes = 0;
info.producer_key = producer_key;
info.is_active = true;
info.url = url;
info.location = location;
});
}
}
//找到相关,删除
void system_contract::unregprod( const account_name producer ) {
require_auth( producer );
const auto& prod = \_producers.get( producer, "producer not found" );
\_producers.modify( prod, 0, [&]( producer_info& info ){
info.deactivate();
});
}
//更新相关出块人
void system_contract::update_elected_producers( block_timestamp block_time ) {
\_gstate.last_producer_schedule_update = block_time;
auto idx = \_producers.get_index<N(prototalvote)>();
std::vector< std::pair<eosio::producer_key,uint16_t> > top_producers;
top_producers.reserve(21);//一票30投,但只取21,后49备用,再后忽略
for ( auto it = idx.cbegin(); it != idx.cend() && top_producers.size() < 21 && 0 < it->total_votes && it->active(); ++it ) {
top_producers.emplace_back( std::pair<eosio::producer_key,uint16_t>({{it->owner, it->producer_key}, it->location}) );
}
if ( top_producers.size() < \_gstate.last_producer_schedule_size ) {
return;
}
/// sort by producer name
std::sort( top_producers.begin(), top_producers.end() );
std::vector<eosio::producer_key> producers;
producers.reserve(top_producers.size());
for( const auto& item : top_producers )
producers.push_back(item.first);
bytes packed_schedule = pack(producers);
if( set_proposed_producers( packed_schedule.data(), packed_schedule.size() ) >= 0 ) {
\_gstate.last_producer_schedule_size = static_cast<decltype(\_gstate.last_producer_schedule_size)>( top_producers.size() );
}
}
/**
* An account marked as a proxy can vote with the weight of other accounts which
* have selected it as a proxy. Other accounts must refresh their voteproducer to
* update the proxy's weight.
*
* @param isproxy - true if proxy wishes to vote on behalf of others, false otherwise
* @pre proxy must have something staked (existing row in voters table)
* @pre new state must be different than current state
*/
//注册成代理人
void system_contract::regproxy( const account_name proxy, bool isproxy ) {
require_auth( proxy );
auto pitr = \_voters.find(proxy);
if ( pitr != \_voters.end() ) {
eosio_assert( isproxy != pitr->is_proxy, "action has no effect" );
eosio_assert( !isproxy || !pitr->proxy, "account that uses a proxy is not allowed to become a proxy" );
\_voters.modify( pitr, 0, [&]( auto& p ) {
p.is_proxy = isproxy;
});
propagate_weight_change( *pitr );
} else {
\_voters.emplace( proxy, [&]( auto& p ) {
p.owner = proxy;
p.is_proxy = isproxy;
});
}
}
分析投票及相关方法后,开始处理投票的交易动作:
/**
* When a user posts we create a record that tracks the total votes and the time it
* was created. A user can submit this action multiple times, but subsequent calls do
* nothing.
*
* This method only does something when called in the context of the author, if
* any other contexts are notified
*/
void apply_social_post() {
const auto& post = current_action<post_action>();
require_auth( post.author );
eosio_assert( current_context() == post.author, "cannot call from any other context" );
static post_record& existing;
if( !Db::get( post.postid, existing ) )
Db::store( post.postid, post_record( now() ) );
}
/**
* This action is called when a user casts a vote, it requires that this code is executed
* in the context of both the voter and the author. When executed in the author's context it
* updates the vote total. When executed
*/
void apply_social_vote() {
const auto& vote = current_action<vote_action>();
require_recipient( vote.voter, vote.author );
disable_context_code( vote.author() ); /// prevent the author's code from rejecting the potentially negative vote
auto context = current_context();
auto voter = vote.getVoter();
if( context == vote.author ) {
static post_record post;
eosio_assert( Db::get( vote.postid, post ) > 0, "unable to find post" );
eosio_assert( now() - post.created < days(7), "cannot vote after 7 days" );
post.votes += vote.vote_power;
Db::store( vote.postid, post );
}
else if( context == vote.voter ) {
static account vote_account;
Db::get( "account", vote_account );
auto abs_vote = abs(vote.vote_power);
vote_account.vote_power = min( vote_account.social_power,
vote_account.vote_power + (vote_account.social_power * (now()-last_vote)) / days(7));
eosio_assert( abs_vote <= vote_account.vote_power, "insufficient vote power" );
post.votes += vote.vote_power;
vote_account.vote_power -= abs_vote;
vote_account.last_vote = now();
Db::store( "account", vote_account );
} else {
eosio_assert( false, "invalid context for execution of this vote" );
}
}
3、共识
前面的选举过程其实就DPOS的过程,只不过,没有出块,体现不出来它的价值,在EOS的最新版本中采用了BFT-DPOS,所以看下面的数据结构:
struct block_header_state {
......
uint32_t dpos_proposed_irreversible_blocknum = 0;
uint32_t dpos_irreversible_blocknum = 0;
uint32_t bft_irreversible_blocknum = 0; //BFT
......
};
这个变量bft_irreversible_blocknum是在push_confirmation中被赋值。connection::blk_send中广播。
三、出块
出块的代码主要在producer_plugin中:
producer_plugin_impl::start_block_result producer_plugin_impl::start_block() {
......
//省略各种出块条件的前期判断
.......
if (\_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::producing) {
// determine if our watermark excludes us from producing at this point
if (currrent_watermark_itr != \_producer_watermarks.end()) {
if (currrent_watermark_itr->second >= hbs->block_num + 1) {
elog("Not producing block because \"${producer}\" signed a BFT confirmation OR block at a higher block number (${watermark}) than the current fork's head (${head_block_num})",
("producer", scheduled_producer.producer_name)
("watermark", currrent_watermark_itr->second)
("head_block_num", hbs->block_num));
\_pending_block_mode = pending_block_mode::speculating;
}
}
}
try {
uint16_t blocks_to_confirm = 0;
if (\_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::producing) {
// determine how many blocks this producer can confirm
// 1) if it is not a producer from this node, assume no confirmations (we will discard this block anyway)
// 2) if it is a producer on this node that has never produced, the conservative approach is to assume no
// confirmations to make sure we don't double sign after a crash TODO: make these watermarks durable?
// 3) if it is a producer on this node where this node knows the last block it produced, safely set it -UNLESS-
// 4) the producer on this node's last watermark is higher (meaning on a different fork)
if (currrent_watermark_itr != \_producer_watermarks.end()) {
auto watermark = currrent_watermark_itr->second;
if (watermark < hbs->block_num) {
blocks_to_confirm = std::min<uint16_t>(std::numeric_limits<uint16_t>::max(), (uint16_t)(hbs->block_num - watermark));
}
}
}
chain.abort_block();
chain.start_block(block_time, blocks_to_confirm);//调用真正的Controller.cpp出块
} FC_LOG_AND_DROP();
......
}
//时间调度不断循环出块
void producer_plugin_impl::schedule_production_loop() {
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin<chain_plugin>().chain();
\_timer.cancel();
std::weak_ptr<producer_plugin_impl> weak_this = shared_from_this();
auto result = start_block();//出块
if (result == start_block_result::failed) {
elog("Failed to start a pending block, will try again later");
\_timer.expires_from_now( boost::posix_time::microseconds( config::block_interval_us / 10 ));
// we failed to start a block, so try again later?
\_timer.async_wait([weak_this,cid=++_timer_corelation_id](const boost::system::error_code& ec) {
auto self = weak_this.lock();
if (self && ec != boost::asio::error::operation_aborted && cid == self->_timer_corelation_id) {
self->schedule_production_loop();
}
});
} else if (\_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::producing) {
\_timer.async_wait([&chain,weak_this,cid=++_timer_corelation_id](const boost::system::error_code& ec) {
auto self = weak_this.lock();
if (self && ec != boost::asio::error::operation_aborted && cid == self->_timer_corelation_id) {
auto res = self->maybe_produce_block();//完成出块
fc_dlog(\_log, "Producing Block #${num} returned: ${res}", ("num", chain.pending_block_state()->block_num)("res", res) );
}
});
......
} else if (\_pending_block_mode == pending_block_mode::speculating && !\_producers.empty() && !production_disabled_by_policy()){
// if we have any producers then we should at least set a timer for our next available slot
optional<fc::time_point> wake_up_time;
for (const auto&p: \_producers) {
auto next_producer_block_time = calculate_next_block_time(p);
if (next_producer_block_time) {
auto producer_wake_up_time = \*next_producer_block_time - fc::microseconds(config::block_interval_us);
if (wake_up_time) {
// wake up with a full block interval to the deadline
wake_up_time = std::min<fc::time_point>(\*wake_up_time, producer_wake_up_time);
} else {
wake_up_time = producer_wake_up_time;
}
}
}
if (wake_up_time) {
.......
} else {
......
}
} else {
fc_dlog(\_log, "Speculative Block Created");
}
}
//在操作中断时启动异步出块
bool producer_plugin_impl::maybe_produce_block() {
auto reschedule = fc::make_scoped_exit([this]{
//退出本范围重新启动正常出块
schedule_production_loop();
});
try {
produce_block();//出块
return true;
} FC_LOG_AND_DROP();
//处理异常时的出块
fc_dlog(\_log, "Aborting block due to produce_block error");
chain::controller& chain = app().get_plugin<chain_plugin>().chain();
chain.abort_block();
return false;
}
void producer_plugin_impl::produce_block() {
......
//idump( (fc::time_point::now() - chain.pending_block_time()) );
chain.finalize_block();// 完成出块---下面是签名和提交块
chain.sign_block( [&]( const digest_type& d ) {
auto debug_logger = maybe_make_debug_time_logger();
return signature_provider_itr->second(d);
} );
chain.commit_block();
......
}
真正的出块是在controller.hpp.cpp中,需要注意的是按照EOS一惯的风格,真正的代码在controller_impl类中:
void start_block( block_timestamp_type when, uint16_t confirm_block_count, controller::block_status s ) {
FC_ASSERT( !pending );
FC_ASSERT( db.revision() == head->block_num, "",
("db.revision()", db.revision())("controller_head_block", head->block_num)("fork_db_head_block", fork_db.head()->block_num) );
auto guard_pending = fc::make_scoped_exit([this](){
pending.reset();
});
//创建pending,块在其中
pending = db.start_undo_session(true);
pending->_block_status = s;
pending->_pending_block_state = std::make_shared<block_state>( \*head, when ); // promotes pending schedule (if any) to active
pending->_pending_block_state->in_current_chain = true;
pending->_pending_block_state->set_confirmed(confirm_block_count);
auto was_pending_promoted = pending->_pending_block_state->maybe_promote_pending();
//判断当前的状态并设置相关参数
const auto& gpo = db.get<global_property_object>();
if( gpo.proposed_schedule_block_num.valid() && // if there is a proposed schedule that was proposed in a block ...
( *gpo.proposed_schedule_block_num <= pending->_pending_block_state->dpos_irreversible_blocknum ) && // ... that has now become irreversible ...
pending->_pending_block_state->pending_schedule.producers.size() == 0 && // ... and there is room for a new pending schedule ...
!was_pending_promoted // ... and not just because it was promoted to active at the start of this block, then:
)
{
// Promote proposed schedule to pending schedule.
if( !replaying ) {
ilog( "promoting proposed schedule (set in block ${proposed_num}) to pending; current block: ${n} lib: ${lib} schedule: ${schedule} ",
("proposed_num", \*gpo.proposed_schedule_block_num)("n", pending->_pending_block_state->block_num)
("lib", pending->_pending_block_state->dpos_irreversible_blocknum)
("schedule", static_cast<producer_schedule_type>(gpo.proposed_schedule) ) );
}
pending->_pending_block_state->set_new_producers( gpo.proposed_schedule );
db.modify( gpo, [&]( auto& gp ) {
gp.proposed_schedule_block_num = optional<block_num_type>();
gp.proposed_schedule.clear();
});
}
try {
//装填交易的实际数据
auto onbtrx = std::make_shared<transaction_metadata>( get_on_block_transaction() );
push_transaction( onbtrx, fc::time_point::maximum(), true, self.get_global_properties().configuration.min_transaction_cpu_usage );
} catch( const boost::interprocess::bad_alloc& e ) {
elog( "on block transaction failed due to a bad allocation" );
throw;
} catch( const fc::exception& e ) {
wlog( "on block transaction failed, but shouldn't impact block generation, system contract needs update" );
edump((e.to_detail_string()));
} catch( ... ) {
wlog( "on block transaction failed, but shouldn't impact block generation, system contract needs update" );
}
clear_expired_input_transactions();//清除相关交易
update_producers_authority();//更新生产者相关的权限
guard_pending.cancel();//解除锁
}
finalize_block 、sign_block、 commit_block 、abort_block等与签名和提交部分的代码都在这个模块中,就不再赘述,看代码就可以了。